 the total body mass of humans; in an adult having 65 kilograms of mass (143 lbs), bone marrow typically accounts for approximately 2.6 kilograms (5.7 lb). The hematopoietic component of bone marrow produces approximately 500 billion blood cells per day, which use the bone marrow vasculature as a conduit to the body’s systemic circulation. Bone marrow is also a key component of the lymphatic system, producing the lymphocytes that support the body’s immune system.
the total body mass of humans; in an adult having 65 kilograms of mass (143 lbs), bone marrow typically accounts for approximately 2.6 kilograms (5.7 lb). The hematopoietic component of bone marrow produces approximately 500 billion blood cells per day, which use the bone marrow vasculature as a conduit to the body’s systemic circulation. Bone marrow is also a key component of the lymphatic system, producing the lymphocytes that support the body’s immune system.
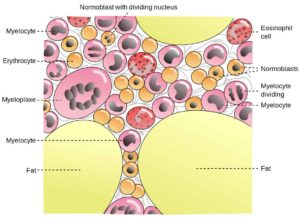
The two types of bone marrow are “red marrow” (Latin: medulla ossium rubra), which consists mainly of hematopoietic tissue, and “yellow marrow” (Latin: medulla ossium flava), which is mainly made up of fat cells. Red blood cells, platelets, and most white blood cells arise in red marrow. Both types of bone marrow contain numerous blood vessels and capillaries. At birth, all bone marrow is red. With age, more and more of it is converted to the yellow type; only around half of adult bone marrow is red. Red marrow is found mainly in the flat bones, such as the pelvis, sternum, cranium, ribs, vertebrae and scapulae, and in the cancellous (“spongy”) material at the epiphyseal ends of long bones such as the femur and humerus. Yellow marrow is found in the medullary cavity, the hollow interior of the middle portion of short bones. In cases of severe blood loss, the body can convert yellow marrow back to red marrow to increase blood cell production.

